AI Copilots - Copilots
AI Copilots provides a default copilot for testing, but you should define a custom copilot in the Liveblocks dashboard for further development and production. This allows you to configure your AI model, system prompt, back-end knowledge, and more.
Creating a copilot
To create a copilot, open the Liveblocks dashboard, select a project and click on the “AI Copilots” page. Click on the “Create copilot” button, and fill in the required fields.
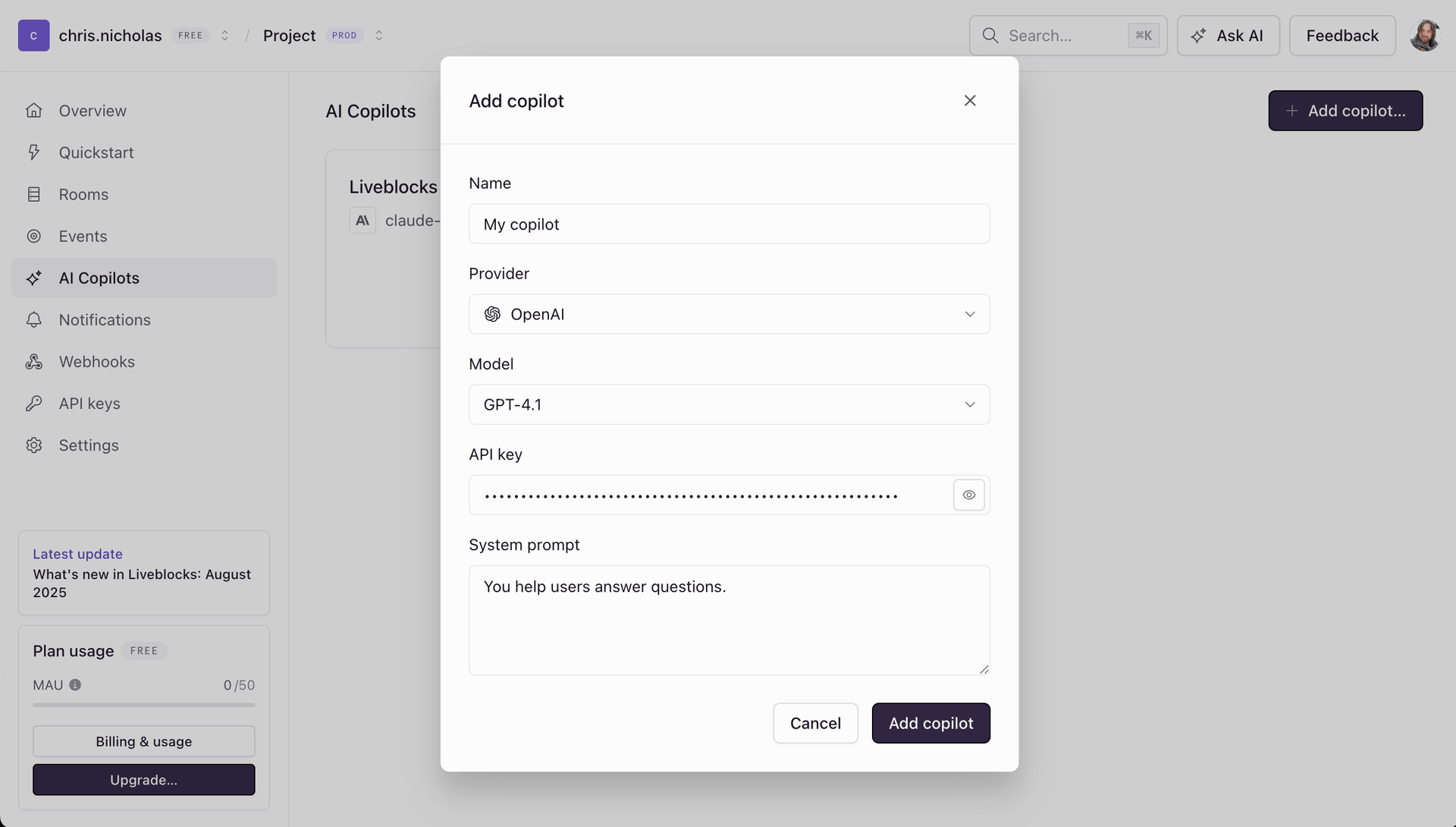
Get your API key
Copilots use API keys provided by your AI provider, which can be created and copied on their respective websites. Out of the box, we support OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, but, you can use other OpenAI-compatible APIs, such as Groq and OpenRouter.
Add the copilot to your application
To use the new copilot in your application, copy your copilot ID from the dashboard.
Paste the copilot ID into
AiChat and
useSendAiMessage to
start using it.
Configuring your copilot
Within the “General” tab you can configure a number of settings for your copilot. Settings slightly differ between providers.
Name
The name of your AI Copilot, which will be displayed in the dashboard.
Provider
This is the AI provider you want to use for your copilot. You can choose from OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, and other OpenAI-compatible APIs, such as Groq. Using an OpenAI-compatible tool like OpenRouter allows you to define fallback models.
Model
The AI model you want to use for your copilot, such as GPT-4.1 or
Claude 4 Sonnet. You can choose from the models supported by your provider.
With third-party tools you can
define fallback models.
Custom provider name
If you’re using an OpenAI-compatible provider, you can define a custom provider name, which you may find on your provider’s website. If a custom provider name isn’t needed by your provider, you can use any string.
Base URL
If you’re using an OpenAI-compatible provider, you must define a base URL, which you can find on your provider’s website.
Reasoning effort, extended thinking, thinking budget
Reasoning is supported by some models, allowing AI show its thought processes,
and come up with more accurate answers. Some models allow you to select a
reasoning effort, such as low, medium, or high, or a token budget for
extended thinking.
Web search
Toggle web searching, allowing your AI to query the internet for information.
Limit web search to specific domains
When web search is enabled, limit the domains that the AI can search. Will
search both http:// and https:// URLs. Subdomains are allowed.
API key
The API key for your provider. You can find keys on each provider’s website: OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. Also supports OpenAI-compatible APIs, such as Groq and OpenRouter. All API keys are encrypted at rest, and never stored in plain text.
System prompt
The system prompt defines the behavior of the copilot, for example:
You can create more complex system prompts by using Markdown formatting.
When should AI use knowledge?
This setting determines when AI will search back-end knowledge before responding.
You can also write a more complex prompt, giving knowledge a name, which then allows you to refer to it in your system prompt. This can help reinforce AI behavior.
Adding back-end knowledge
Under the “Knowledge” tab you can add back-end knowledge to your copilot. Knowledge can be submitted as web pages or files, and your AI chat can query this knowledge when responding, allowing it to intelligently answer questions or perform tasks.
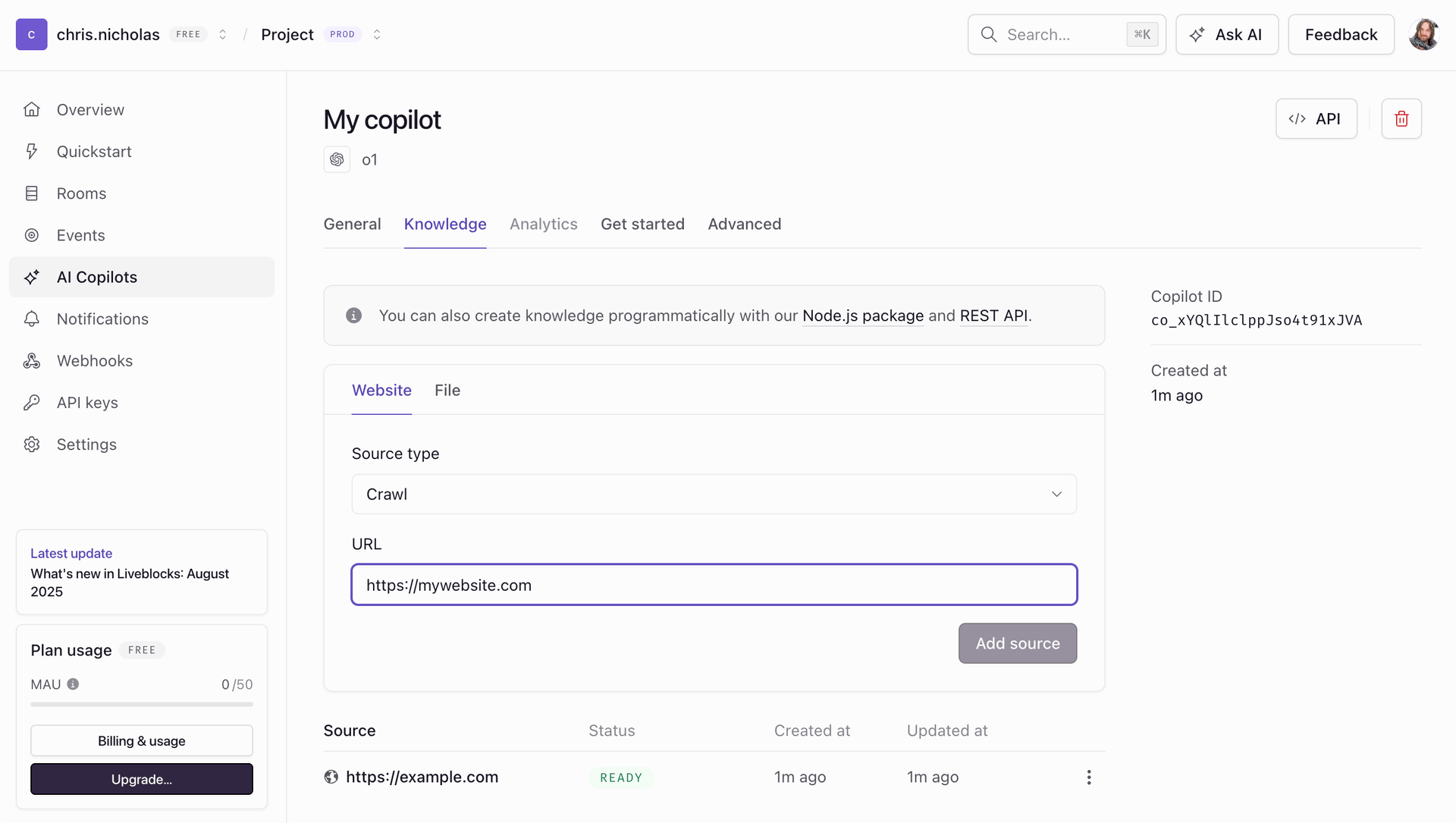
You can submit a whole website/sitemap for crawling, a single page, or PDF/image files. Crawled knowledge is not updated, and to update it, it must be resubmitted programmatically or via the dashboard.
Configuring advanced settings
Under the “Advanced” tab you can configure a number of advanced settings for your copilot. By default, Liveblocks does not pass default values to your provider, and leaves the options blank.
| Setting | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|
| Max tokens | Controls response length | 1024 |
| Temperature | Controls randomness in responses | 0.2 |
| Top P | Alternative to temperature for controlling randomness | 0.9 |
| Top K | Advanced sampling control | 200 |
| Presence penalty | Controls repetition of existing content | 0.3 |
| Frequency penalty | Controls repetition of words and phrases | 0.3 |
| Stop sequences | Controls when text generation stops | ["\\n\\n", "Human:"] |
| Seed | Controls randomness for reproducible results | 42 |
| Max retries | Controls how many times to retry failed requests | 2 |
Modifying copilots programmatically
You aren’t limited to creating copilots from the dashboard—you can also create and modify copilots programmatically, allowing users or teams in your app to have their own individual copilots.
This is made possible using the Liveblocks Node.js client and REST API, where a number of APIs are available for managing copilots.
You can also manage each copilot’s knowledge sources.