Authentication - Set up ID token permissions with Next.js
Follow the following steps to start configure your authentication endpoint and
start building your own security logic in Next.js’ /app directory.
Quickstart
Install the
liveblocks/nodepackageSet up authentication endpoint
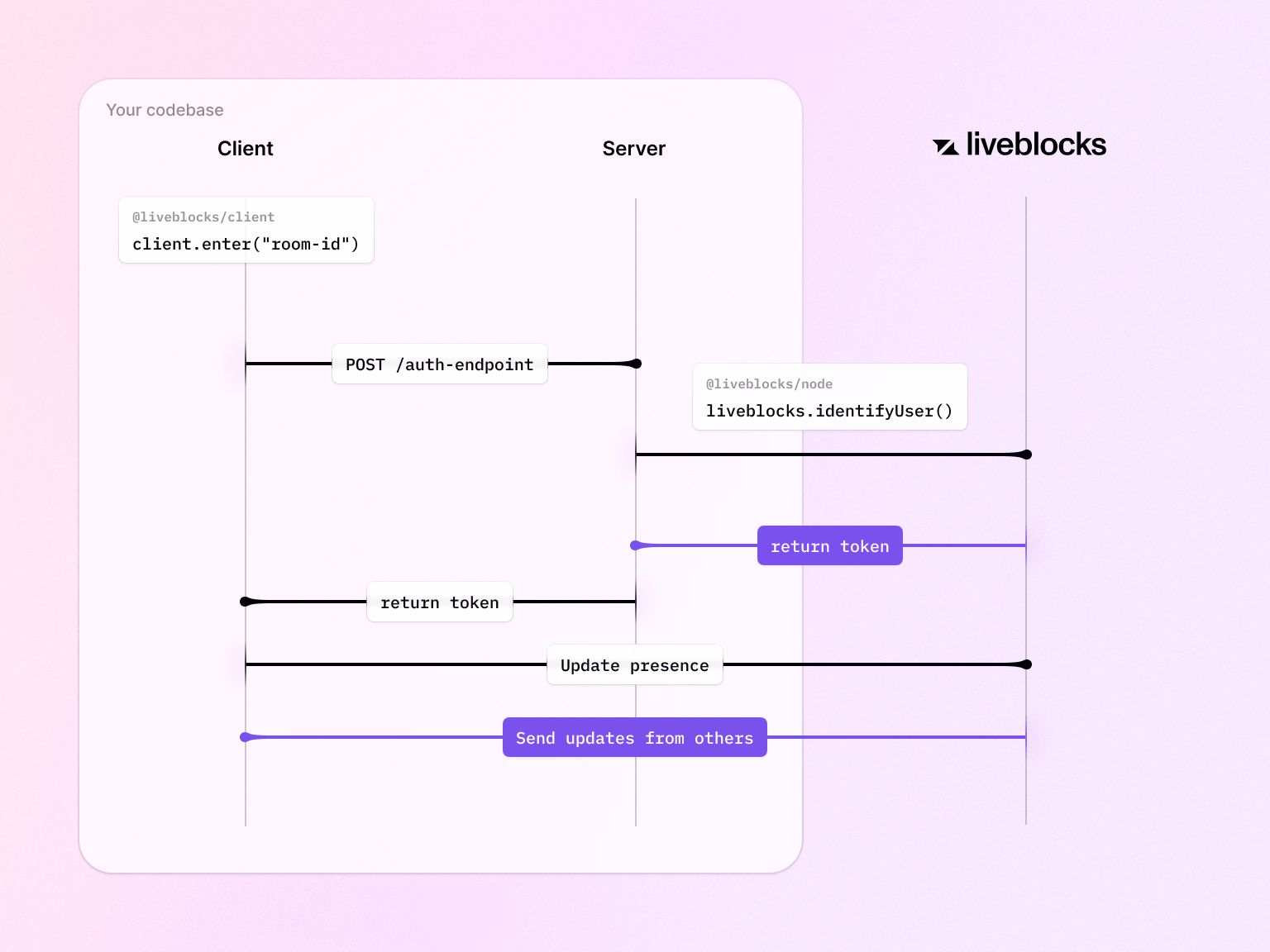
Users can only interact with rooms they have access to. You can configure permission access in an
api/liveblocks-authendpoint by creating theapp/api/liveblocks-auth/route.tsfile with the following code. This is where you will implement your security and define if the current user has access to a specific room.app/api/liveblocks-auth/route.tsHere’s an example using the older API routes format in
/pages.Set up the client
On the front end, you can now replace the
publicApiKeyprop onLiveblocksProviderwithauthEndpointpointing to the endpoint you just created.If you need to pass custom headers or data to your endpoint, you can use authEndpoint as a callback instead.
Set permission accesses to a room
A room can have
defaultAccesses,usersAccesses, andgroupsAccessesdefined. Permissions are then checked when users try to connect to a room. For security purposes, room permissions can only be set on the back-end through@liveblocks/nodeor our REST API. For instance, you can useliveblocks.createRoomto create a new room with read-only public access levels while giving write access to specific groups and users.For more information, make sure to read the section on room permissions.
Attach metadata to users
Optionally, you can attach static metadata to each user, which will be accessible in your app. First you need to define the types in your config file, under
UserMeta["info"].liveblocks.config.tsWhen authenticating, you can then pass the user’s metadata to
prepareSessionin the endpoint we’ve just created.app/api/liveblocks-auth/route.tsUser metadata has now been set! You can access this information in your app through
useSelf.Bear in mind that if you’re using the default Comments components, you must specify a
nameandavatarinuserInfo.
More information
Both userId and userInfo can then be used in your React application as such: